Using external mesh files¶
Here we describe how to import external mesh files created in CAD or other modeling tools as models into Choreonoid. In this example, we use Blender, a free modeling tool, to create a mesh, but you can also import meshes created with other CAD tools or modeling tools using the same process.
Tank model¶
Here we will look at mesh import for the Tank model, which is an advanced version of the SimpleTank Model. The Tank model consists of the five parts shown in the figure below.
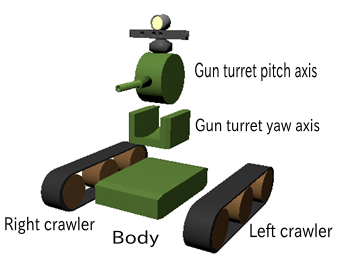
The base part is the chassis. On top of the chassis are the turret and gun barrel. This part consists of two sections: one that serves as the foundation for the turret and performs yaw axis rotation, and another section that is mounted on top with the gun barrel and performs pitch axis rotation. Crawlers are attached to the left and right sides of the chassis respectively.
These five parts are modeled. The chassis part is the central part of the model and is modeled as the “parent object”. The turret yaw axis part and crawler parts are modeled as child objects of the parent chassis, and the turret pitch axis part is modeled as a child object of the turret yaw axis part. In addition, the gun barrel mounted on the turret and devices such as cameras and lights are also modeled.
The hierarchical structure (parent-child relationships) between these objects is as follows:
- Chassis
+ Turret yaw axis part
+ Turret pitch axis part
+ Left crawler
+ Right crawler
First, create the shape of this model using CAD tools or 3D-CG tools such as Blender.
Setting parent-child relationships¶
Set the parent-child relationships between each shape that makes up the Tank model in the modeling tool.
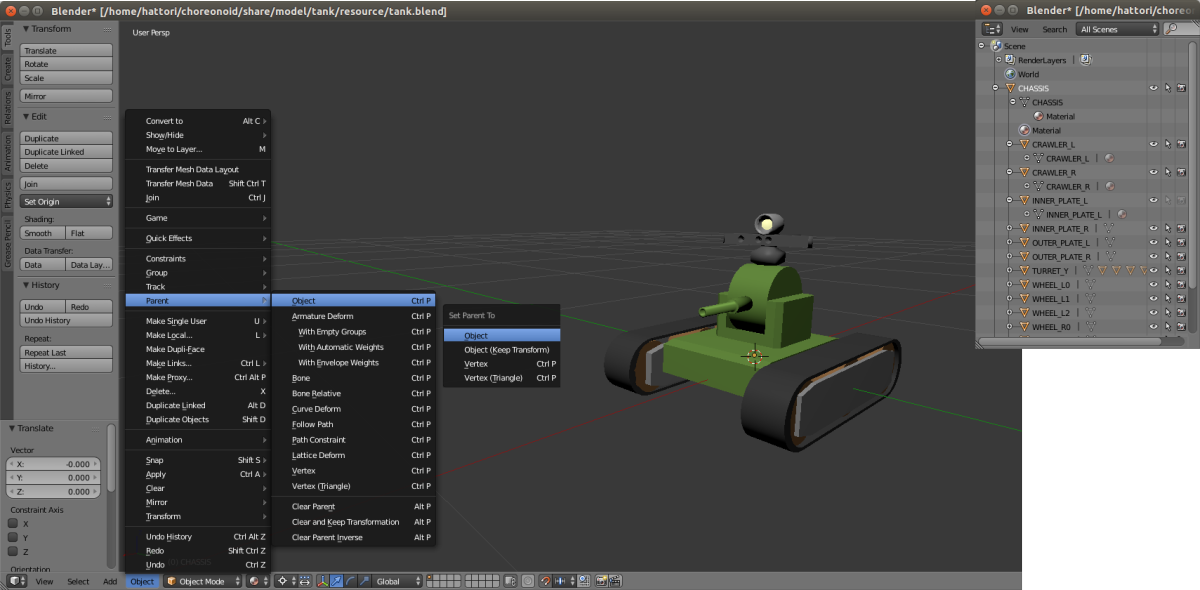
In the case of Blender, first select the object that will be the child. Next, select the object that will be the parent, then select “3D View Header” ⇛ “Object” ⇛ “Parent” ⇛ “Object”. The parent target window will be displayed, so select “Object” to complete the parent-child relationship setting. When you set parent-child relationships, they will be displayed in a hierarchical structure in the “Outliner”.
Setting object names¶
To import the shape of each link from Choreonoid, assign names to each shape in the modeling tool in advance.
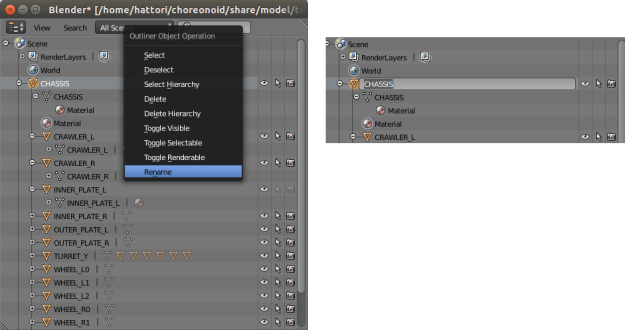
In the case of Blender, you can change the object name by “right-clicking” on an object displayed in the “Outliner” ⇛ “Rename”.
Exporting model files¶
Once you have finished creating the model, export the model to a file format that can be read by Choreonoid.
Formats that can be read include Collada (.dae) and VRML97. Other formats such as STL and OBJ can also be read by Choreonoid, but these formats do not include the model structure (parent-child relationships), so they cannot be used when exporting the entire model consisting of multiple links at once as in this case. (It is possible to import them if you export each link as separate files.)
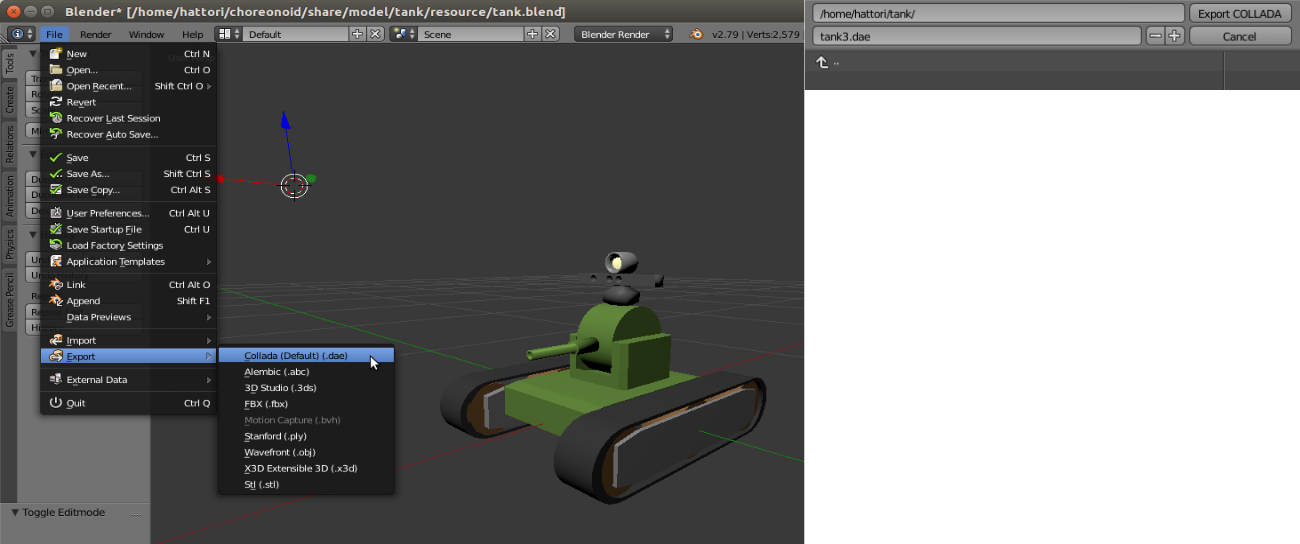
Here we will export the entire model created in Blender in Collada format (.dae). Select “Menu Bar” ⇛ “File” ⇛ “Export” ⇛ “Collada (Default) (.dae)”, enter a filename, and press “Export COLLADA”.
Loading model files in YAML format files¶
By describing the resource under elements as shown below, you can load the created model file and display it in Choreonoid. The exported model file contains the contents of the entire Tank model. By specifying the object name set on the modeling tool side for the node key, you can import and display only the shape of the target object.
Also, by specifying Visual for the node type, it can be described as a display model, and by specifying Collision, it can be described as a collision model.
links:
-
name: CHASSIS
translation: [ 0, 0, 0.1 ]
jointType: free
centerOfMass: [ 0, 0, 0 ]
mass: 8.0
inertia: [
0.1, 0, 0,
0, 0.1, 0,
0, 0, 0.5 ]
elements:
-
type: Visual
resource:
uri: "resource/tank3.dae"
node: CHASSIS
-
type: Collision
elements:
-
type: Shape
translation: [ 0.0, 0.0, 0.0 ]
geometry: { type: Box, size: [ 0.375, 0.3, 0.1 ] }
-
type: Shape
translation: [ 0.20625, 0.0, 0.0 ]
geometry: { type: Box, size: [ 0.0375, 0.3, 0.08 ] }
-
type: Shape
translation: [ 0.205, 0.0, 0.04 ]
rotation: [ 0, 1, 0, 15 ]
geometry: { type: Box, size: [ 0.03881, 0.3, 0.01 ] }
-
type: Shape
translation: [ 0.205, 0.0, -0.04 ]
rotation: [ 0, 1, 0, -15 ]
geometry: { type: Box, size: [ 0.03881, 0.3, 0.01 ] }
-
type: Shape
translation: [ -0.20625, 0.0, 0.0 ]
geometry: { type: Box, size: [ 0.0375, 0.3, 0.08 ] }
-
type: Shape
translation: [ -0.205, 0.0, 0.04 ]
rotation: [ 0, 1, 0, -15 ]
geometry: { type: Box, size: [ 0.03881, 0.3, 0.01 ] }
-
type: Shape
translation: [ -0.205, 0.0, -0.04 ]
rotation: [ 0, 1, 0, 15 ]
geometry: { type: Box, size: [ 0.03881, 0.3, 0.01 ] }