Multicopter Simulation Plugin¶
The multicopter simulation plugin can simply simulate propulsion force and physical effects the behavior of a flying multicopter. This plugin mainly consists of the following two functions.
- A function to simulate the rotor device mounted on the multicopter.
- A function to simulate the influence of the air (buoyance, additional mass, additional moment of inertia, surface force) on the multicopter.
Here, we will explain the following items.
- Introduction of Multicopter Simulation Plugin
- Setting of Body Model
- Setting of Item MulticopterSimulatorItem.
Introduction of Multicopter Simulation Plugin¶
The option below has to be enabled in the configuration of CMake for building choreonoid.
- BUILD_MULTICOPTER_PLUGIN
Setting of Body Model¶
Add the following configurations to the Body model for executing the multicopter simulation.
- MulticopterTargetBody
- MulticopterTargetLink
- RotorDevice
As an example, a simple multicopter model is located at Choreonoid derectory /share/model/Multipopter/ if multicopter simulation plugin is installed. Refer to the model file for how to set the configurations.
Setting of MulticopterTargetBody¶
“MulticopterTargetBody” is the node that indicates that a Body model describing it is a target Body model for applying multicopter simulation. By describing this node, MulticopterTargetLink node and RotorDevice node are linked in the target Body model.
Example of the description of MulticopterTargetBody
format: ChoreonoidBody
formatVersion: 1.0
angleUnit: degree
name: Multicopter
MultiCopterTargetBody:
cutoffDistance: -1
normMiddleValue: -1
Below is the definition of MulticopterTargetBody node.
| Key | Unit | Function |
|---|---|---|
| cutoffDistance | [m] | The distance used for cutoff calculation. By specifying -1, cutoff calculation is not performed. |
| normMiddleValue | [-] | The median used for cutoff calculation. By specifying -1, cutoff calculation is not performed. |
The child items cutoffDistance and normMiddleValue are parameters to prevent the surface force given to each link of the Body model from overlapping calculation. The frictional force applied between the air and the body of the multicopter when the body of the multicopter contacts the air and the pressure acting on the body surface of the multicopter are reflected in the surface force. This plugin calculates the surface force for each surface of the link. When the Body model consists of one link as indicated in the figure below (left), the surface force simply applies to the link. On the other hand, when an arbitrary Body model consists of two links connecting to each other (including the case where one includes the other) as indicated in the figure below (right), the surface force is given to each of the links, and accordingly the surface force can occur inside the Body model as well.
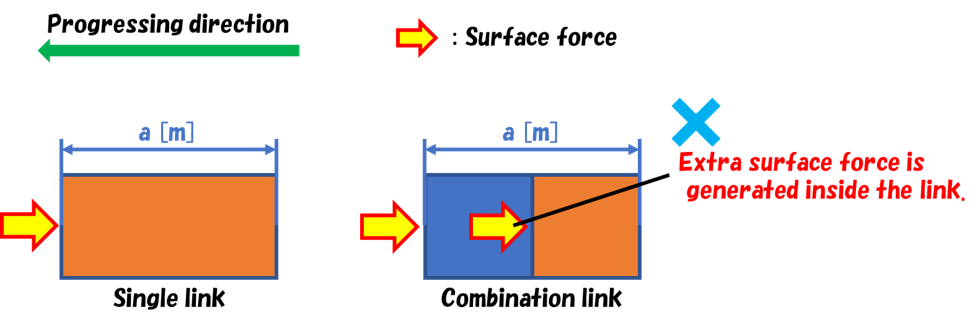
Therefore, this plugin applies the calculation to specify the regions for applying the surface force to the targeted links (called cutoff calculation) based on the distance between the surfaces of the links, when the surface of a link is close to or included in the surface of another link. In this calculation, when the distance between the surfaces of the links is smaller than the value specified in cutoffDistance [m], the surface force is applied in proportion. The normMiddleValue, for which the value between 0~1 is supposed to be set, is a parameter to determine the rate of the surface force given to the links when the distance between the surfaces of the links is the same as the value of cutoffDistance or smaller. Normally, it set it to 0.5. Thus, the surface force is determined in proportion in accordance with the distance between the surfaces of the links.
This process is necessary only in the case of using a Body model of complex configuration. When you do not need to use this, and therefore set cutoffDistance and normMiddleValue to -1 so as to avoid execution of this calculation.
Setting of MulticopterTargetLink¶
MulticopterTargetLink is the node that indicates that links describing it are target links of the multicopter simulation. Buoyancy, additional mass, additional moment of inertia, and surface force are given as external force to the links describing this node. If this node is not set, such calculations are not performed.
Example of description of MulticopterTargetLink
MultiCopterTargetLink:
applyForce: [ true, true, true, true ]
density: 250
centerOfBuoyancy: [ 0.0, 0.0, 0.0 ]
additionalMassCoef: 0.1
additionalInertiaMatrix: [
0.00041, 0, 0,
0, 0.00041, 0,
0, 0, 0.00066 ]
Below is the definition of MultcopterTargetLink node.
| Key | Unit | Function |
|---|---|---|
| applyForce | [-] | Chooses true/false for enabling/disabling buoyancy, additional mass, additional moment of inertia, and surface force. This parameter can be omitted and. In that case, buoyancy, additional mass, additional moment of inertia, and surface force are all set to true. |
| density | [kg/m^3] | The density of the link. |
| centerOfBuoyancy | [m, m, m] | The center of buoyancy in the local coordinate system. This parameter can be omitted and. In that case, buoyance is given to the center of the link. |
| additionalMassCoef | [-] | Specifies the additional mass coefficient. |
| additionalInertiaMatrix | [-] | The additional moment of inertia. |
Setting of RotorDevice¶
RotorDevice node defines the rotor device. As is the case in other devices, RotorDevice node can attached on each of the links that compose the Body model, and it can be used by setting the definition under the elements of the links.
Setting of RotorDevice
elements:
-
type: RotorDevice
name: droneRotor1
position: [ 0, 0, 0 ]
direction: [ 0, 0, 1 ]
valueRange: [ -10, 10 ]
torqueRange: [ -10, 10 ]
effectParameter:
wallDistance: 1.0
wallNormMiddleValue: 0.5
wallMaxRate: 0.5
groundDistance: 1.0
groundNormMiddleValue: 0.5
groundMaxRate: 0.5
Below is the definition of RotorDevice.
| Key | Function |
|---|---|
| type | Specifies “RoterDevice”. |
| name | The name of an arbitrary rotor device. |
| position | The position of point which propulsion works on to the original point of the link. If it is set to [0,0,0], propulsion acts on the origin of the link. |
| direction | The direction of propulsion of the rotor device. If it is set to [0,0,1], propulsion acts upwardly in the z-axis direction of the local coordinate system. |
| valueRange | The minimum and maximum output values of the propulsion of the rotor device [N]. |
| torqueRange | The minimum and maximum torque values of the antitorque by the rotor device [Nm]. |
| effectParameter | This tag is necessary for simulating the effects which are supposed to be caused when the multicopter gets close to the ceiling, floor or wall, such as clinging and being attracted. If you do not set this tag, simulation of such effects is not applying, and therefore there is no need to set the following items: wallDistance, wallNormMiddleValue, wallMaxRate, groundDistance, groundNormMiddleValue, and groundMaxRate. |
| wallDistance | When the Body model approaches the wall model closer than the distance of this parameter [m], horizontal force acts on the rotor device in the way that the Body model is attracted toward the wall model. |
| wallNormMiddleValue | This is a parameter to decide how to apply the horizontal force when the Body model approaches the wall model closer than the wallDistance. Set it to 0.5 normally. Thus, the horizontal force acting on the rotor device is determined in proportion in accordance with the distance. |
| wallMaxRate | Specifies the rate of the horizontal force given to the rotor device. When it is 1.0, the horizontal force applied to the rotor device equals the power of the rotor device, and when it is 0.5, the force is half of the power of the rotor device. |
| groundDistance | When the Body model approaches the ceiling/floor model closer than the distance of this parameter [m], force in vertical direction acts on the rotor device in the way that it is pushed away from the floor. |
| groundNormMiddleValue | This is a parameter to decide how to apply the vertical force when the Body model approaches the ceiling/floor model closer than the groundDistance. Set it to 0.5 normally. Thus, the vertical force acting on the rotor device is determined in proportion in accordance with the distance. |
| groundMaxRate | Specifies the rate of the vertical force given to the rotor device. When it is 1.0, the vertical force applied to the rotor device equals the power of the rotor device, and when it is 0.5, the force is half of the power of the rotor device. |
I/O of RotorDevice¶
For input and output of the rotor device set for the Body model, include the following header in the program of the controller.
#include <cnoid/RotorDevice>
As the RotoDevice node is defined in the namespace “Multicopter”, you need to write as follows.
using namespace Multicopter;
For setting the pointer of each RotorDevice class, describe the line like example below.
RotorDevice* rotordevice;
Store in the created pointer the pointer of RotorDevice set for the Body model. The example below is to store the pointer of “RotorDevice1” using findDevice method of Body class.
rotordevice = io->body()->findDevice<RotorDevice>("RotorDevice1");
Input the propulsion and the torque by the rotor device. The example below is the input of propulsion 1.0 [N] and torque 1.0 [Nm].
rotordevice->setValue(1.0);
rotordevice->setTorque(1.0);
Finally, execute the line below to reflect the propulsion and the torque by the rotor device in the simulation.
rotordevice->notifyStateChange();
Setting of MulticopterSimulatorItem¶
The multicopter simulation uses on item named ad MulticopterSimulatorItem. Choose “MulticopterSimulator” from “File” - “New…” of the main menu, and create MulticopterSimulatorItem. By default, it is named as “MulticopterSimulator”. Allocate it as a child item of the simulator item in the item tree view. The multicopter simulation is corresponding to AIST simulator and AGX simulator.
Example of the configuration of MulticopterSimulatorItem
[ ] - World
[/] + Multicopter
[/] + floor
[ ] + AISTSimulator
[ ] + MulticopterSimulatorItem
Setting items of MulticopterSimulator¶
It is necessary to set the property of MulticopterSimulatorItem for simulating the multicopter. Below is the description of each property.
| Property | Unit | Function |
|---|---|---|
| Fluid Density | [kg/m^3] | Specifies the air density. |
| Viscosity | [Pa*s] | Specifies the air viscosity. |
| Fluid Velocity | [m/s, m/s, m/s] | Specifies the regular fluid velocity. |
| Air Definition File | [-] | Specifies the definition file (AirDefinitionFile) that File specifies an area in the simulation space and gives partially air density, air viscosity and regular fluid velocity. Regular fluid specified at “Fluid Velocity” is applied outside the area specified by this file. |
| Wall Effect | [-] | Enables/disables the effect to be pulled to the wall. |
| Ground Effect | [-] | Enables/disables the ground effect. |
| Output Parameter | [-] | Enables/disables to display the parameter that is applied to multicopter model to the MulticopterMonitor view. |
| Output Time Step | [s] | The time interval to output the parameter to Step the MulticopterMonitor view. |
Outline of AirDefinitionFile¶
The multicopter simulation allows you to apply air density, air viscosity and regular fluid velocity in an arbitrary area of the simulation space by specifying Air Definition File of the property of MulticopterSimularotItem. Below is the description of Air Definition File.
AirEnvironment,1.0.0
X,-7.5,15,1
Y,-7.5,15,1
Z,0,5,1
"Index(X,Y,Z)",Density,Velocity(X),Velocity(Y),Velocity(Z),Viscosity
"0,0,0",1.293,1,0,0,0.000017
"1,0,0",1.293,1,0,0,0.000017
"0,1,0",1.293,1,0,0,0.000017
"1,1,0",1.293,1,0,0,0.000017
"0,0,1",1.293,1,0,0,0.000017
"1,0,1",1.293,1,0,0,0.000017
"0,1,1",1.293,1,0,0,0.000017
"1,1,1",1.293,1,0,0,0.000017
| Key | Function |
|---|---|
| AirEnvironment | Indicates the file version. In general, you don’t need to edit this item. |
| X, Y, Z | Specifies the each axis direction of the specified area. They indicate “reference coordinate in the global coordinate system [m]”, “computation grid interval [m]” and “number of computation grid [unit]”, respectively, starting from the left. The example is the definition of the space extending 15 [m] in the X direction, 15 [m] in the Y direction and 5 [m] in the Z direction setting the reference point to (-7.5, -7.5, 0) of the global coordinate. |
| Index | Index of the coordinate of computation grid. The value obtained by adding index multiplied by computation grid interval to the reference point is the global coordinate of the vertex of the computation grid indicated by the index. In the case of the example above, index [0,0,0] and index [0,0,1] indicate the vertex of the computation grid in the global coordinate (-7.5,-7.5,0) and (-7.5,-7.5,5), respectively. |
| Density | Specify the density [kg/m^3] given to the computation grid. |
| Velocity | Specify the velocity [m/s] given to the computation grid. |
| Viscosity | Specify the viscosity [Pa*s] given to the computation grid. |
Sample project for Multicopter Simulation¶
There is a sample project using MulticopterPlugin in Choreonoid directory “samples/Multicopter”. To make it available, turn on the following CMake option when building Choreonnoid and MulticopterPlugin.
- BUILD_MULTICOPTER_SAMPLES
The file of the sample project is QuadcopterJoystick.cnoid, which uses the quadcopter model and simple controller.
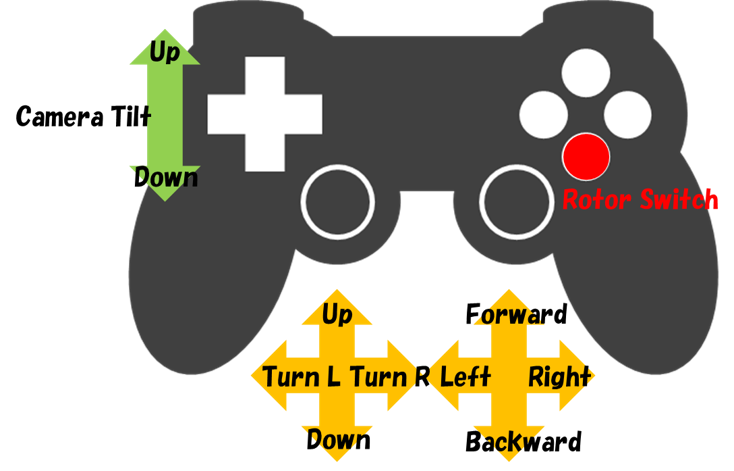
Key assignment for operating of the sample multicopter of this sample is set as below, in the case of operating with DUAL SHOCK4 of PS4.